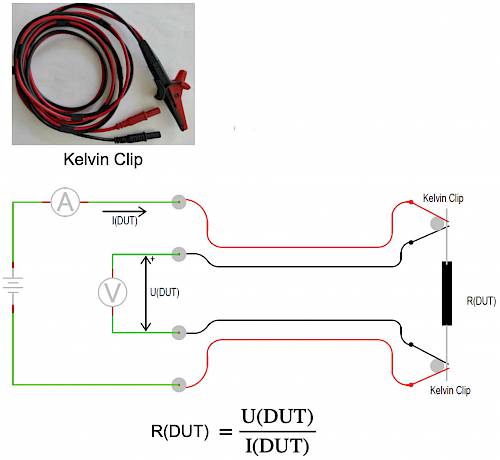
The Kelvin or 4-Wire measurement method is the resistance measurement method which avoids errors caused by the resistance of test probes (wires). Therefore, it is possible to accurately measure very low resistance values (e.g. < 0.1 Ω). During measurement, an unknown resistance (DUT) is connected to measurement instrument using a pair of special type of aligator clips called "Kelvin clips", where the jaw halves are insulated from each other at the hinge point and only contacting at the tips where they clasp the wire or terminal of the DUT being measured. Thus, current through the “current” jaw halves does not go through the “voltage” jaw halves, and will not create any error-inducing voltage drop along their length.
A continuity test of the earth conductor aka “Earth Continuity Test” must be performed regularly for all Class I appliances. It ensures that there is a satisfactory connection between the earth pin in a plug and the case of the appliance. In order to achive its protective duty, earth conductor should have very low resistance and must withstand very high currents in case of a fault situation. In order to check continuity of the earth conductor, usualy an instrument based on the Kelvin method utilizing high a AC test current (> 10A) is used. So, not only resistance of the Earth conductor is measured, but also the conductor is stressed out and checked how and if it can withstand a high current that would occur in the event of a fault such as a breakdown in the insulation of the appliance.